In This Article
We often encounter situations where we need to extract specific portions of text that lie between two substrings. This task, while seemingly simple, can be approached in several ways. We will explore three different ways in Python to find a string between two strings. We will also look at a real-world example of how these methods can be applied to extract text from HTML tags.
Find a string between two strings Using the find Method and String Slicing in Python
The find method in Python is a built-in string method that returns the index of the start of the first occurrence of the specified value. It returns -1 if the value is not found.
String slicing, on the other hand, is a way to get a range of characters (substring) from the original string.
The provided Python code defines a function find_all_strings that takes three parameters: text, startsub, and endsub. The text parameter is the string from which we want to extract substrings. startsub and endsub are the substrings that define the start and end of the substrings we want to extract.
def find_all_strings(text, startsub, endsub):
results = []
startidx = 0
while startidx < len(text):
startidx = text.find(startsub, startidx)
if startidx == -1: # startsub not found, stop searching
break
startidx += len(startsub) # move the start index after the startsub
endidx = text.find(endsub, startidx)
if endidx == -1: # endsub not found, stop searching
break
results.append(text[startidx:endidx]) # append the found string to results
startidx = endidx + len(endsub) # move the start index after the endsub for next search
return results
text = "During her vacation, she discovered a hidden beach. As the sun set, she discovered it was the perfect spot for photography. She set up her camera and captured the beautiful sunset."
startsub = "discovered"
endsub = "set"
print(find_all_strings(text, startsub, endsub))Python Code explanation
The function find_all_strings works by initializing an empty list results and a variable startidx at 0. It then enters a while loop that continues until startidx is less than the length of the text.
Inside the loop, it uses the find method to find the index of the start of the first occurrence of startsub in the text starting from startidx. If startsub is not found, it breaks the loop. Otherwise, it moves the startidx to the position right after startsub.
Next, it finds the index of the start of the first occurrence of endsub in the text starting from startidx. If endsub is not found, it breaks the loop. Otherwise, it appends the substring from startidx to endidx in the text to the results list and moves the startidx to the position right after endsub.
Finally, it returns the results list which contains all the substrings found between startsub and endsub.
When the function find_all_strings is called with the provided text and startsub as "discovered" and endsub as "set", it prints:

This output is a list of all substrings in the text that are found between "discovered" and "set". The order of the substrings in the list corresponds to their order of occurrence in the text. The substrings do not include "discovered" and "set" themselves. If there were no such substrings in the text, the list would be empty.
Find a string between two strings using the split Method
Another approach to extracting substrings between two other substrings within a larger string is by using the split method in Python. The split method divides a string into a list where each word is a separate element in the list.
The split method in Python is a built-in string method that splits a string into a list where each word is a separate element. It takes a separator as an argument and splits the string at each occurrence of this separator.
Note: If the separator is not provided, any whitespace (space, newline, etc.) string is a separator.
In the example Python code given below, a function is defined, find_all_strings that takes three parameters: text, start_str, and end_str. The text parameter is the string from which we want to extract substrings. start_str and end_str are the substrings that define the start and end of the substrings we want to extract.
def find_all_strings(text, start_str, end_str):
parts = text.split(start_str)
results = []
for part in parts[1:]:
remaining_text_parts = part.split(end_str, 1)
if len(remaining_text_parts) == 2:
substring = remaining_text_parts[0]
results.append(substring)
return results
text = "On a sunny day, she noticed a little puppy. While it played in the park, she noticed it had a blue collar. She played fetch with it and noticed it was very energetic. After they played, fetch became their favorite game."
start_str = "noticed"
end_str = "played"
print(find_all_strings(text, start_str, end_str))Python Code explanation
The function find_all_strings works by splitting the text at each occurrence of start_str. This results in a list of parts. For each part after the first, it splits the part at the first occurrence of end_str. If the part contains end_str, it appends the substring before end_str to the results list. Finally, it returns the results list which contains all the substrings found between start_str and end_str.
When the function find_all_strings is called with the provided text and start_str as "noticed" and end_str as "played", it prints:

This output is a list of all substrings in the text that are found between "noticed" and "played". The order of the substrings in the list corresponds to their order of occurrence in the text.
Extracting Substrings Using Regular Expressions in Python
Regular expressions (regex) are a powerful tool for manipulating text. They provide a flexible way to search and match string patterns within larger text strings. In Python, the re module provides support for regular expressions and is part of the standard library.
The re.findall method in Python is used to find all occurrences of a pattern in a string. The method returns a list of all matches of the pattern. If the pattern is not found, re.findall returns an empty list.
The Python code below defines a function find_all_strings that uses regular expressions to find all substrings between two other substrings within a larger string. The function takes three parameters: text, startsub, and endsub.
The text parameter is the string from which we want to extract substrings. startsub and endsub are the substrings that define the start and end of the substrings we want to extract.
import re
def find_all_strings(text, startsub, endsub):
s = str(re.escape(startsub))
e = str(re.escape(endsub))
matches = re.findall(f'{s}(.*?){e}', text)
return matches
text = "In the morning she saw a beautiful bird. Suddenly, it flew away. She saw it fly over the tall trees. It flew into the clear sky."
startsub = "saw"
endsub = "flew"
print(find_all_strings(text, startsub, endsub))The function find_all_strings works by first escaping any special characters in startsub and endsub using the re.escape function. It then constructs a regex pattern that matches any text that starts with startsub and ends with endsub. The .*? in the pattern is a non-greedy match that matches any characters except newline (.) as few times as possible (*?) until endsub is encountered. The re.findall function is then used to find all matches of this pattern in the text. The matches are returned as a list.
When the function find_all_strings is called with the provided text and startsub as "saw" and endsub as "flew", it prints:

This output is a list of all substrings in the text that are found between all occurrences of the pair “saw” and “flew”.
In the next section, we will show an example of making use of one of the methods to handle a realistic case.
Real-world application of Python to find a string between two strings
Extracting Text from HTML Using Python
In the world of web scraping and data extraction, it’s often necessary to extract specific pieces of information from HTML content. One common task is to extract the text contained within paragraph tags (<p> and </p>). In this section, we’ll explore a Python script that accomplishes this task using regular expressions.
The script uses the re module in Python, which provides support for regular expressions, a powerful tool for matching and manipulating text. The re.findall function is used to find all occurrences of a pattern in a string, returning them as a list.
The provided Python code defines three functions: find_all_strings, extract_text_between_p_tags, and main.
import re
import pprint
def find_all_strings(text, startsub, endsub):
s = str(re.escape(startsub))
e = str(re.escape(endsub))
matches = re.findall(f'{s}(.*?){e}', text)
return matches
def extract_text_between_p_tags(html_text):
start_tag = '<p>' end_tag = '</p>' return find_all_strings(html_text, start_tag, end_tag) def main(): with open('page.html', 'r') as file: html_text = file.read() extracted_text = extract_text_between_p_tags(html_text) print("Text between <p> tags:") pprint.pprint(extracted_text) if __name__=="__main__": main() The find_all_strings function takes three parameters: text, startsub, and endsub. It constructs a regular expression pattern that matches any text that starts with startsub and ends with endsub, and uses re.findall to find all matches of this pattern in text.
The extract_text_between_p_tags function calls find_all_strings with <p> as startsub and </p> as endsub, effectively finding all text that is between <p> and </p> tags in html_text.
The main function reads the content of an HTML file, 'page.html', and calls extract_text_between_p_tags with this content. It then prints the extracted text, which is a list of all text between <p> and </p> tags in the HTML file.
The HTML file we are to read and extract info from, 'page.html', has the following contents:
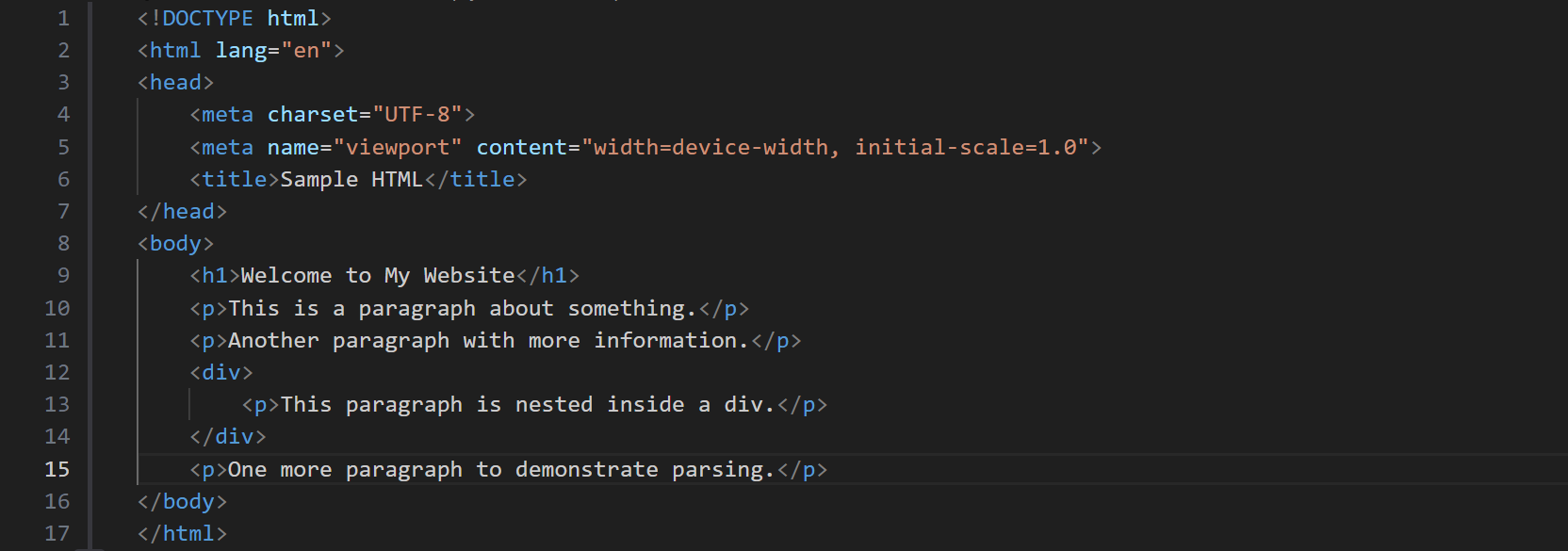
When run, this script reads the HTML file, extracts all text between <p> and </p> tags, and prints this text. The output is a list of strings, where each string is a piece of text that was found between <p> and </p> tags in the HTML file.

Since we made use of pprint, it allowed us to display the list neatly.
In conclusion, Python offers a variety of ways to find a string between two substrings in a text. Whether you choose to use the built-in find function and slicing, the split function, or regular expressions depending on your specific needs. The real-world example of extracting text from HTML tags demonstrates the practical application of these methods.