In This Article
looking for how to perform an alphabetic telephone number translator in Python?
Many businesses use mnemonic phone numbers like 555-GET-FOOD to make their contact information easier to remember. However, these alphabetic representations need to be translated into their numeric equivalents for dialing.
This article will guide you through creating a Python program to perform this translation. We will cover the problem statement, the logic behind the solution, and the step-by-step implementation of the program. Additionally, we will demonstrate the program with multiple examples to ensure a thorough understanding.
Understanding the Problem Statement
The task is to translate a phone number containing alphabetic characters into a purely numeric phone number, as one sees on a standard telephone keypad.
For example, the input 555-GET-FOOD should be translated to 555-438-3663.
This translation is based on the mapping where:
- A, B, C -> 2
- D, E, F -> 3
- G, H, I -> 4
- J, K, L -> 5
- M, N, O -> 6
- P, Q, R, S -> 7
- T, U, V -> 8
- W, X, Y, Z -> 9
The translation mapping from alphabetic characters to numeric digits is based on the layout of the traditional telephone keypad.
Here’s a breakdown of how these mappings were established:
- 2: ABC
- 3: DEF
- 4: GHI
- 5: JKL
- 6: MNO
- 7: PQRS
- 8: TUV
- 9: WXYZ
This system was designed to make dialing easier before the advent of digital keypads.
Each number from 2 to 9 is associated with a group of three or four letters. However, the number 1 is not mapped to any letters. Historically, 1 was reserved for special functions such as connecting to an operator or initiating certain services, which is why it was not associated with any alphabetic characters.
Planning the Solution for Alphabetic Telephone Number Translator
To solve this problem, we will:
- Prompt the user to enter a phone number.
- Translate each alphabetic character to its corresponding number using a dictionary.
- Construct the translated phone number and display it.
Let’s start with the Python code for this task.
def translate_phone_number(phone_number):
# Dictionary to map letters to numbers
letter_to_number = {
'A': '2', 'B': '2', 'C': '2',
'D': '3', 'E': '3', 'F': '3',
'G': '4', 'H': '4', 'I': '4',
'J': '5', 'K': '5', 'L': '5',
'M': '6', 'N': '6', 'O': '6',
'P': '7', 'Q': '7', 'R': '7', 'S': '7',
'T': '8', 'U': '8', 'V': '8',
'W': '9', 'X': '9', 'Y': '9', 'Z': '9'
}
# Convert the phone number
translated_number = ''
for char in phone_number:
if char.isalpha():
translated_number += letter_to_number[char.upper()]
else:
translated_number += char
return translated_number
# Example usage
phone_number = input("Enter a 10-character telephone number in the format XXX-XXX-XXXX: ")
translated_number = translate_phone_number(phone_number)
print("Translated number:", translated_number)
The `translate_phone_number` function takes a phone number as input and uses a dictionary to map each alphabetic character to its numeric equivalent. The function iterates through each character in the input phone number, checking if it is an alphabetic character. If it is, the character is converted to its corresponding number using the dictionary. If it is not an alphabetic character, it remains unchanged. The translated number is then returned.
The main part of the program prompts the user to input a phone number, call the translate_phone_number function, and prints the translated number.
Here is an example of running the program:

The input `555-GET-FOOD` is translated to `555-438-3663` as per the mapping rules defined.
Testing the Program with Various Inputs Alphabetic Telephone Number
We will test the program with different inputs to ensure it works correctly.
Below are ten input cases with their expected outputs.
The following inputs will be tested to demonstrate the functionality of the program:
- 1-800-FLOWERS
- 1800-MY-APPLE
- 123-HELLO-WORLD
- 800-NEW-CAR
- 555-QUICK-FOX
- 777-BIG-BIRD
- 444-DOG-CAT
- 999-SUN-SKY
- 222-FLYING
- 333-HOME-SEC
The following Python code will be used to run the test cases:
test_cases = [
"1-800-FLOWERS",
"1800-MY-APPLE",
"123-HELLO-WORLD",
"800-NEW-CAR",
"555-QUICK-FOX",
"777-BIG-BIRD",
"444-DOG-CAT",
"999-SUN-SKY",
"222-FLYING",
"333-HOME-SEC"
]
for case in test_cases:
print(f"Input: {case}")
print(f"Output: {translate_phone_number(case)}")
print()
When we run the above code, we get the following outputs:
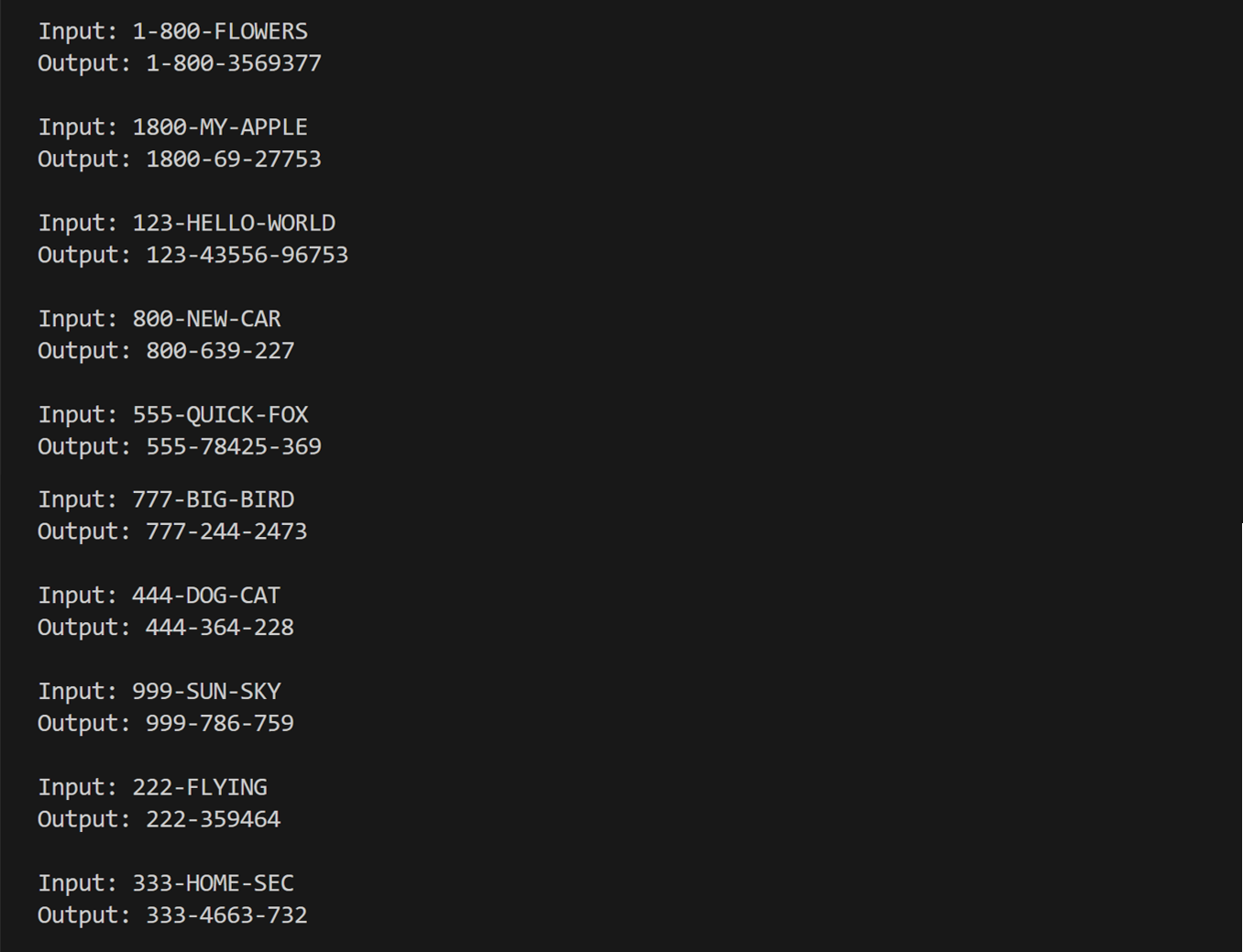
Each of these examples demonstrates how the program accurately translates alphabetic characters in the phone number to their numeric equivalents, preserving the format and readability of the phone number.
For instance, in the case of 1-800-FLOWERS, the program correctly maps each letter to its corresponding number on a telephone keypad, resulting in the output 1-800-3569377. This consistency across different inputs confirms the reliability of the program.
Translating alphabetic phone numbers to numeric equivalents is a practical problem with real-world applications, especially for businesses that use mnemonic phone numbers.
By understanding the mapping of alphabetic characters to their numeric counterparts on a telephone keypad, we can easily automate this translation using Python programming.